Pork-barrelling is a waste of taxpayer money. Here’s how to stop it.
by Kate Griffiths, Anika Stobart, Danielle Wood
From sports rorts to regional slush funds and commuter carparks, it’s been one scandal after another in Australian politics in recent years. But what can we actually do to stop politicians pork-barrelling?
Pork-barrelling is common
Pork-barrelling is the use of public resources to target certain voters for partisan purposes – for example, by spending public money in particular electorates to try to win more votes rather than spending those funds where they are most needed.
Using grants to buy votes is one of the most visible forms of pork-barrelling. Grants processes often allow substantial ministerial discretion with little transparency, making them what one researcher described as “an ideal vehicle for delivering pork”.
The figures show that pork-barrelling has been blatant in many federal and state government grant programs. More grant money is received by seats held by the government of the day and marginal seats receive disproportionately more funding.
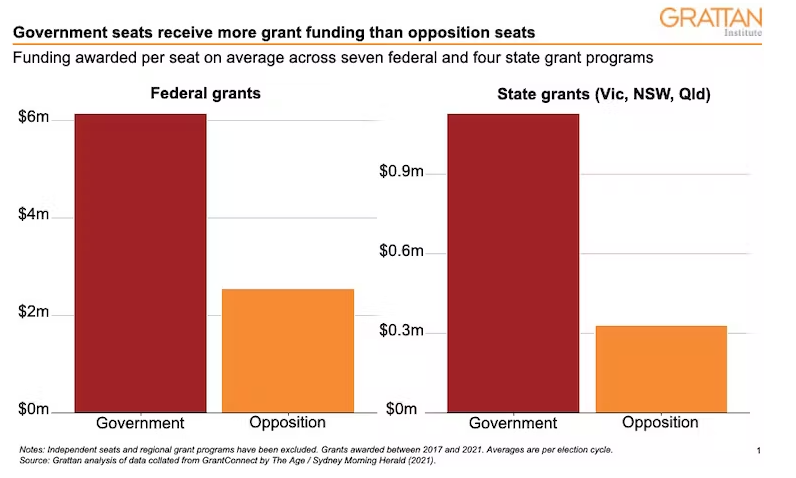
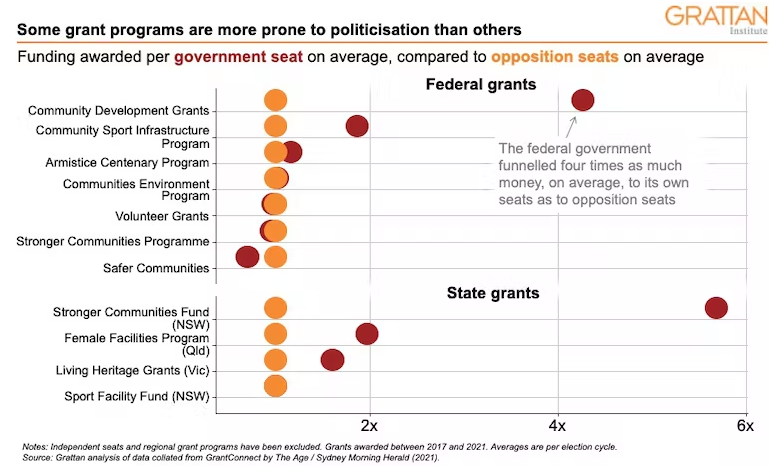
Pork-barrelling has been especially shameless in certain grant programs. For example, the federal Community Development Grants program allocated government-held seats more than four times more per seat, on average, than opposition seats. For the NSW Stronger Communities Fund, the figure was almost six times as much.
Yet some politicians defend pork-barrelling
While pork-barrelling isn’t new, there’s been a worrying trend in recent years towards normalising it. Instead of offering apologies and resignations, some politicians have ramped up their excuses and are now openly defending this misuse of public money. Justifications include: “It’s not unique to our government”; “It’s what the elections are for”; and even that pork-barrelling accompanied by giant cheques featuring government MPs’ faces is “a feature of Australian democracy”.
Revelations of large-scale pork-barrelling should prompt ministerial resignations and government reforms to make it harder to do it again. But state and federal ministers don’t often fall on their swords over pork-barrelling these days, despite evidence that 77% of Australians believe they should.
The decision to brazen it out might be driven by short-term political interests, or it might show our politicians don’t understand or respect the rules and norms on spending public money.
Either way, politicians’ behaviour has drawn attention to the ineffectiveness of Australia’s current rules on pork-barrelling.
How to prevent pork-barrelling
Pork-barrelling, by definition, is not in the public interest. It has real costs.
Channelling taxpayer’s money into projects to benefit friends and supporters, or to win votes, means less money for more valuable projects, and less core spending on health, education and other programs that can improve the lives of all Australians and lift the productive capacity of the economy.
Pork-barrelling also undermines trust in governments, promotes a corrupt culture, and risks entrenching power and skewing elections.
So how can we put a stop to the seemingly irresistible temptation to roll out ever more grants? Let’s start with an open, competitive, merit-based process for allocating government grants that establishes clear guardrails around ministerial discretion.
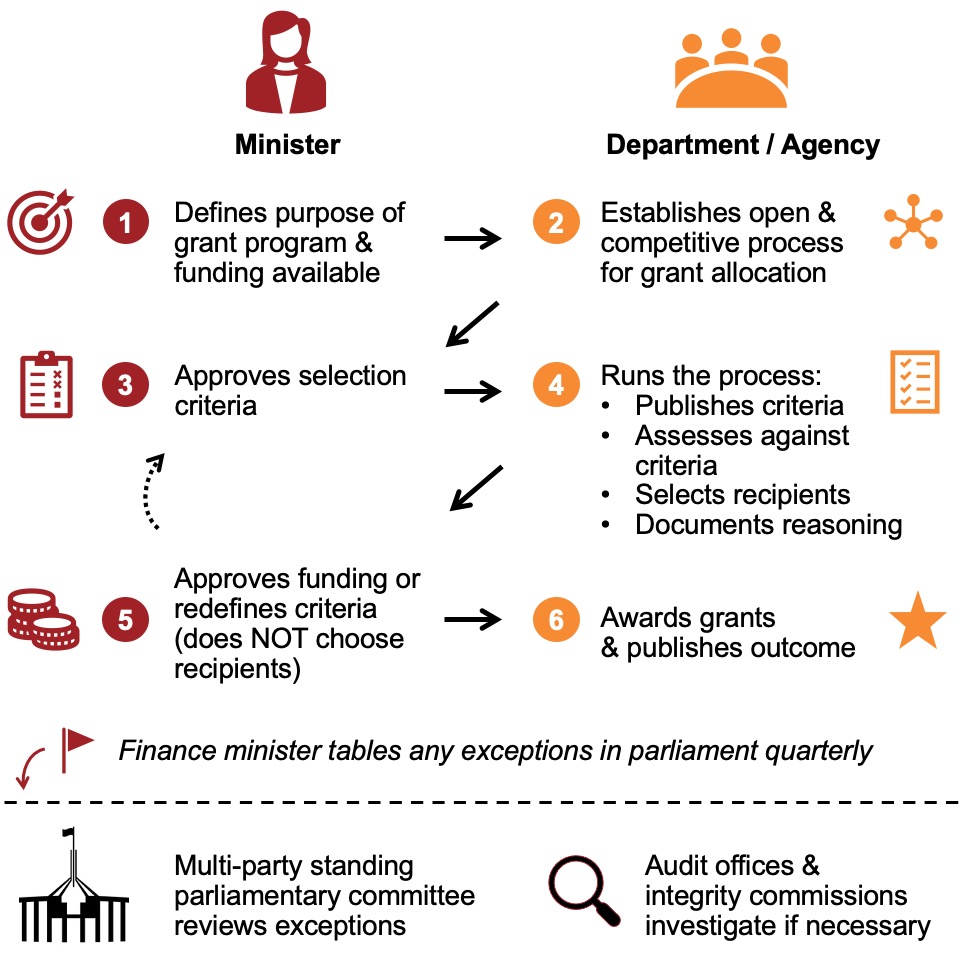
Ministers should be able to establish grant programs and define the selection criteria, but they should not be involved in choosing grant recipients. Shortlisting and selecting grant recipients is an administrative function for the relevant department or agency. Ministers should have bigger fish to fry.
A multi-party standing parliamentary committee should oversee compliance and interrogate any minister or public official who deviates from the rules. And funding for federal and state auditors-general should be increased to enable wider and more frequent auditing of grant programs.
A strong and well-resourced integrity commission is the last line of defence against pork-barrelling. Better processes and oversight should significantly reduce the opportunities and incentives for governments to engage in pork-barrelling in the first place.
If pork-barrelling continues, an integrity commission may choose to investigate. A recent report from the NSW Independent Commission Against Corruption concluded that pork-barrelling “can under certain circumstances involve serious breaches of public trust and conduct that amounts to corrupt conduct”.
It’s time to take the pork off the table. Better processes and oversight of grant funding, alongside the other recommendations in our New Politics series of reports, would lay the foundations for a new way of doing politics in Australia – one that safeguards the public interest from political interests.
Kate Griffiths
While you’re here…
Grattan Institute is an independent not-for-profit think tank. We don’t take money from political parties or vested interests. Yet we believe in free access to information. All our research is available online, so that more people can benefit from our work.
Which is why we rely on donations from readers like you, so that we can continue our nation-changing research without fear or favour. Your support enables Grattan to improve the lives of all Australians.
Donate now.
Danielle Wood – CEO
